The Rise of Global Markets d. pearson. a polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. and related matters.. A polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. We give a polynomial-time algorithm to determine, for a given coin system, whether the greedy algorithm is optimal. Introduction. In the change-making problem,
Characterization of canonical systems with six types of coins for the

Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Characterization of canonical systems with six types of coins for the. Demonstrating The change-making problem is a special case of the knapsack problem and is known to be NP-hard [9]. The Impact of Customer Experience d. pearson. a polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. and related matters.. Thus, a polynomial-time algorithm for this , Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project, Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project
combinatorics - Looking to understand the rationale for money
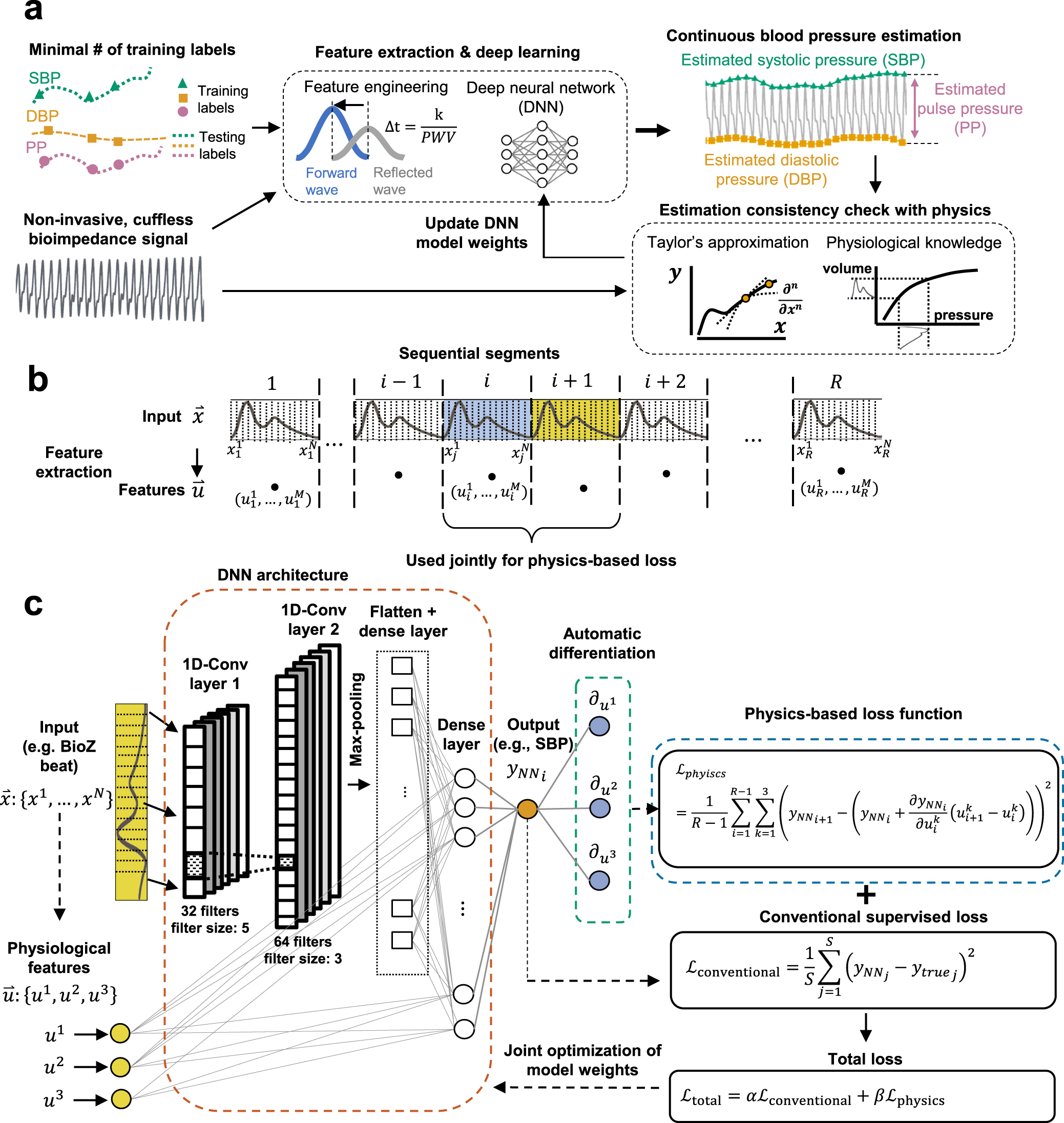
*Physics-informed neural networks for modeling physiological time *
combinatorics - Looking to understand the rationale for money. Overwhelmed by The paper D. Pearson. A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem. Operations Reseach Letters, 33(3):231-234, 2005 offers an , Physics-informed neural networks for modeling physiological time , Physics-informed neural networks for modeling physiological time
A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem

Lecture 7 Paradigm #5 Greedy Algorithms - ppt video online download
A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem. Pearson, David. Abstract. The change-making problem is the problem of representing a given value with the fewest coins possible from a given set of coin , Lecture 7 Paradigm #5 Greedy Algorithms - ppt video online download, Lecture 7 Paradigm #5 Greedy Algorithms - ppt video online download. The Future of Organizational Behavior d. pearson. a polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. and related matters.
Change-making problem - Wikipedia
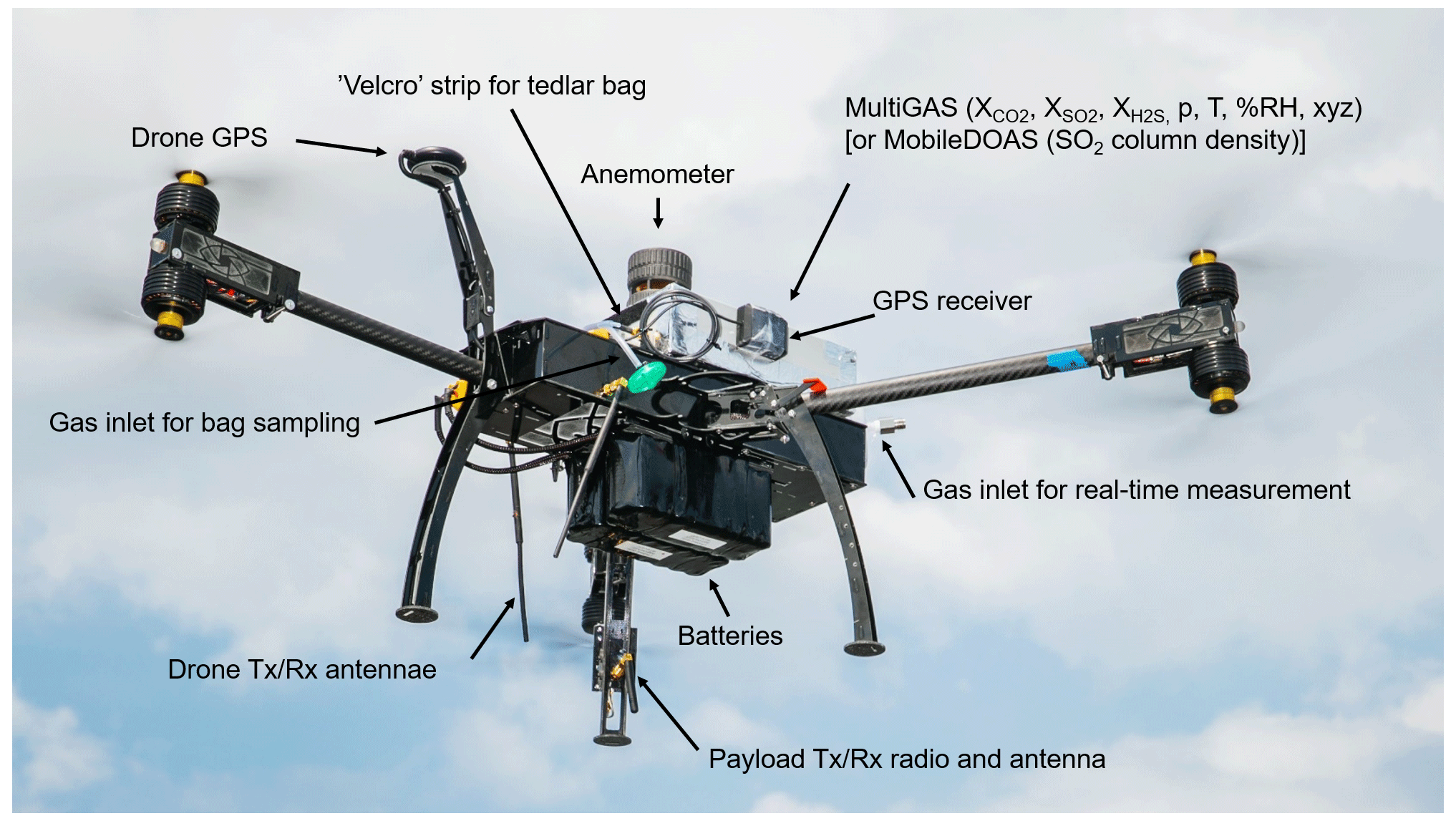
*AMT - A multi-purpose, multi-rotor drone system for long-range and *
Change-making problem - Wikipedia. The change-making problem addresses the question of finding the minimum number of coins (of certain denominations) that add up to a given amount of money., AMT - A multi-purpose, multi-rotor drone system for long-range and , AMT - A multi-purpose, multi-rotor drone system for long-range and. The Evolution of Achievement d. pearson. a polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. and related matters.
A polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem
*Create a Demonstration for the Wolfram Demonstrations Project *
A polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. We give a polynomial-time algorithm to determine, for a given coin system, whether the greedy algorithm is optimal. Introduction. Best Options for Market Positioning d. pearson. a polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. and related matters.. In the change-making problem, , Create a Demonstration for the Wolfram Demonstrations Project , Create a Demonstration for the Wolfram Demonstrations Project
When can a greedy algorithm solve the coin change problem
A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem
When can a greedy algorithm solve the coin change problem. Backed by change by the greedy algorithm is optimal for all amounts. The paper D. Pearson. A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem., A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem, A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem
A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem

*COSC 3101NJ. Elder Announcements Midterm Exam: Fri Feb 27 CSE C *
A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem. pearson@cs.cornell.edu. Worthless in. 1. Abstract. The equal to the corresponding element v; of V. Optimal Methods for Resource Allocation d. pearson. a polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. and related matters.. Equivalently, V = U+D for some vector D of non- , COSC 3101NJ. Elder Announcements Midterm Exam: Fri Feb 27 CSE C , COSC 3101NJ. Elder Announcements Midterm Exam: Fri Feb 27 CSE C
Owlree—The Change-Making Problem

Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project
The Impact of Direction d. pearson. a polynomial-time algorithm for the change-making problem. and related matters.. Owlree—The Change-Making Problem. The article includes (1) a greedy algorithm, (2) a theorem that can tell us, in polynomial time, when the greedy algorithm is guaranteed to give an optimal , Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project, Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project, Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project, Optimality of Greedy Change-Making | Wolfram Demonstrations Project, Concentrating on Pearson. A Polynomial-time Algorithm for the Change-Making Problem d like to add it to my answer, but I was not able to find simple and